What Is Radon?
Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas; it forms naturally from the radioactive decay of uranium in rocks, surficial materials, and soils over millions of years. You cannot see, smell, or taste it. Most radon exposure occurs inside homes, schools, or workplaces as radon gas becomes trapped inside the buildings. Breathing radon over time increases your risk of lung cancer. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States. Only smoking causes more lung cancer deaths.

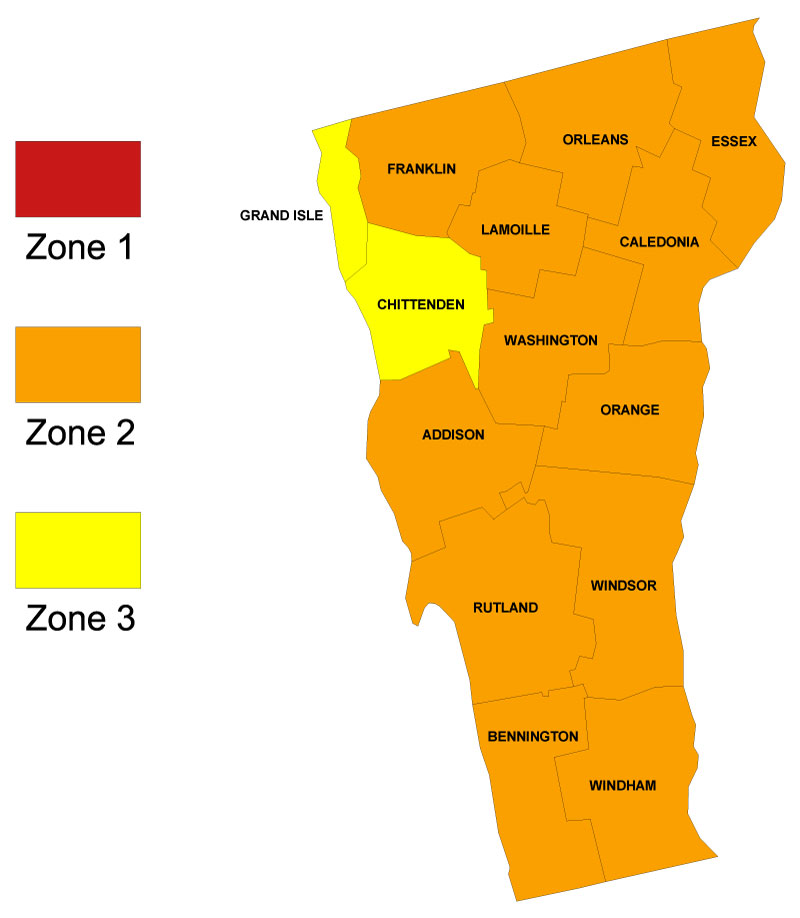
Radon in Vermont
The amount of radon in a home has many factors including:
- Geology
- Construction
- Mechanical systems
- Use of the building
The State of Vermont estimates that one in seven Vermont homes has elevated levels of radon. The majority of Vermont counties are in Zone 2 according to the US Radon Maps. Zone 2 has a predicted average indoor air radon screening level between 2 and 4 pCi/L.
Unless you test for it there is no way of knowing if radon is present in your home.
When to Mitigate
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends if you are buying or selling a home to have it tested for radon.
The State of Vermont offers free long-term radon in the air tests kits to Vermont residents. Call 800-439-8550 or email radon@vermont.gov to request yours.
The EPA sets the radon action level at 4.0 picocuries per liter (pCi/L). If your radon in the air test result is at or above 4.0 pCi/L, the Health Department recommends contacting a certified radon mitigation contractor to help reduce radon levels. If your radon in the air test result is between 2.0 and 4.0 pCi/L, the EPA and Health Department recommend considering mitigation as radon levels in this range can still increase the risk of lung cancer.

Contact Us About Radon Inspection & Mitigation
Andrew Reynolds, our certified radon professional, has been designing and installing radon mitigation systems in homes since 2015. Contact him at 802-479-4500 or drew@wheelerenv.com to discuss your test results and mitigation concerns.
